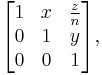Inoue surface
In complex geometry, a part of mathematics, the term Inoue surface denotes several complex surfaces of Kodaira class VII. They are named after Masahisa Inoue, who gave the first non-trivial examples of Kodaira class VII surfaces in 1974.[1]
The Inoue surfaces are not Kähler manifolds.
Contents |
Inoue surfaces with b2 = 0
Inoue introduced three families of surfaces, S0, S+ and S−, which are compact quotients of 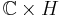 (a product of a complex plane by a half-plane). These Inoue surfaces are solvmanifolds. They are obtained as quotients of
(a product of a complex plane by a half-plane). These Inoue surfaces are solvmanifolds. They are obtained as quotients of 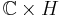 by a solvable discrete group which acts holomorphically on
by a solvable discrete group which acts holomorphically on  .
.
The solvmanifold surfaces constructed by Inoue all have second Betti number 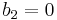 . These surfaces are of Kodaira class VII, which means that they have
. These surfaces are of Kodaira class VII, which means that they have 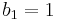 and Kodaira dimension
and Kodaira dimension 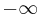 . It was proven by Bogomolov,[2] Li-Yau [3] and Teleman[4] that any surface of class VII with b2 = 0 is a Hopf surface or an Inoue-type solvmanifold.
. It was proven by Bogomolov,[2] Li-Yau [3] and Teleman[4] that any surface of class VII with b2 = 0 is a Hopf surface or an Inoue-type solvmanifold.
These surfaces have no meromorphic functions and no curves.
K. Hasegawa [5] gives a list of all complex 2-dimensional solvmanifolds; these are complex torus, hyperelliptic surface, Kodaira surface and Inoue surfaces S0, S+ and S−.
The Inoue surfaces are constructed explicitly as follows.[5]
Inoue surfaces of type S0
Let φ be an integer 3 × 3 matrix, with two complex eigenvalues 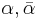 and a real eigenvalue c, with
and a real eigenvalue c, with 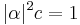 . Then φ is invertible over integers, and defines an action of the group
. Then φ is invertible over integers, and defines an action of the group 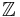 of integers on
of integers on 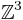 . Let
. Let 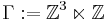 . This group is a lattice in solvable Lie group
. This group is a lattice in solvable Lie group
-
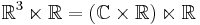 ,
,
acting on 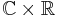 , with the
, with the 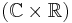 -part acting by translations and the
-part acting by translations and the 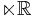 -part as
-part as 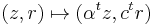 .
.
We extend this action to 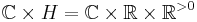 by setting
by setting 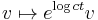 , where t is the parameter of the
, where t is the parameter of the 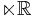 -part of
-part of 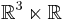 , and acting trivially with the
, and acting trivially with the 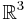 factor on
factor on 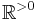 . This action is clearly holomorphic, and the quotient
. This action is clearly holomorphic, and the quotient 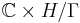 is called Inoue surface of type S0.
is called Inoue surface of type S0.
The Inoue surface of type S0 is determined by the choice of an integer matrix φ, constrained as above. There is a countable number of such surfaces.
Inoue surfaces of type S+
Let n be a positive integer, and 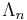 be the group of upper triangular matrices
be the group of upper triangular matrices
where x, y, z are integers. Consider an automorphism of 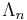 , denoted as φ. The quotient of
, denoted as φ. The quotient of 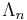 by its center C is
by its center C is 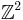 . We assume that φ acts on
. We assume that φ acts on 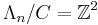 as a matrix with two positive real eigenvalues a, b, and ab = 1.
as a matrix with two positive real eigenvalues a, b, and ab = 1.
Consider the solvable group 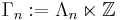 , with
, with 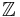 acting on
acting on 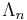 as φ. Identifying the group of upper triangular matrices with
as φ. Identifying the group of upper triangular matrices with 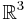 , we obtain an action of
, we obtain an action of 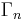 on
on 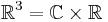 . Define an action of
. Define an action of 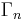 on
on 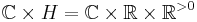 with
with 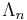 acting trivially on the
acting trivially on the 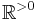 -part and the
-part and the 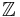 acting as
acting as 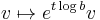 . The same argument as for Inoue surfaces of type
. The same argument as for Inoue surfaces of type 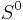 shows that this action is holomorphic. The quotient
shows that this action is holomorphic. The quotient 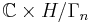 is called Inoue surface of type
is called Inoue surface of type 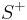 .
.
Inoue surfaces of type S−
Inoue surfaces of type 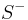 are defined in the same was as for S+, but two eigenvalues a, b of φ acting on
are defined in the same was as for S+, but two eigenvalues a, b of φ acting on 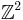 have opposite sign and satisfy ab = −1. Since a square of such an endomorphism defines an Inoue surface of type S+, an Inoue surface of type S− has an unramified double cover of type S+.
have opposite sign and satisfy ab = −1. Since a square of such an endomorphism defines an Inoue surface of type S+, an Inoue surface of type S− has an unramified double cover of type S+.
Parabolic and hyperbolic Inoue surfaces
Parabolic and hyperbolic Inoue surfaces are Kodaira class VII surfaces defined by Iku Nakamura in 1984.[6] They are not solvmanifolds. These surfaces have positive second Betti number. They have spherical shells, and can be deformed into a blown-up Hopf surface.
Parabolic Inoue surfaces are also known as half-Inoue surfaces. These surfaces can be defined as class VII0 (that is, class VII and minimal) surfaces with an elliptic curve and a cycle of rational curves.
Hyperbolic Inoue surfaces are class VII0 surfaces with two cycles of rational curves.[7]
Notes
- ^ M. Inoue, On surfaces of class VII0, Inventiones math., 24 (1974), 269–310.
- ^ Bogomolov, F.: Classification of surfaces of class VII0 with b2 = 0, Math. USSR Izv 10, 255–269 (1976)
- ^ Li, J., Yau, S., T.: Hermitian Yang-Mills connections on non-Kahler manifolds, Math. aspects of string theory (San Diego, Calif., 1986), Adv. Ser. Math. Phys. 1, 560–573, World Scientific Publishing (1987)
- ^ Teleman, A.: Projectively flat surfaces and Bogomolov's theorem on class VII0-surfaces, Int. J. Math., Vol. 5, No 2, 253–264 (1994)
- ^ a b Keizo Hasegawa Complex and Kahler structures on Compact Solvmanifolds, J. Symplectic Geom. Volume 3, Number 4 (2005), 749–767.
- ^ I. Nakamura, On surfaces of class VII0 with curves, Inv. Math. 78, 393–443 (1984).
- ^ I. Nakamura: Survey on VII0 surfaces, Recent Developments in NonKaehler Geometry, Sapporo, 2008 March.